Independent Research Reveals Minecraft’s Global Player Base and Its Impact on Learning Through Play
Independent research reveals that Minecraft has evolved far beyond its origins as a sandbox video game.
NEW YORK CITY, NY, UNITED STATES, December 22, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Independent research by minecraftbuildinginc.com analyzing publicly available data, long-term player trends, and educational use cases reveals that Minecraft has evolved far beyond its origins as a sandbox video game. With a global player base spanning all age groups and increasing adoption in educational environments, the game now represents a measurable intersection between digital play, creativity, and learning.
Originally released in 2009, Minecraft has remained one of the most widely played video games worldwide for over a decade. Player activity data indicates sustained growth rather than decline, with major increases observed between 2018 and 2020. By late 2019, the game was attracting over 112 million active monthly players, with further growth recorded in subsequent years. This continued expansion suggests long-term relevance in both entertainment and educational contexts.
> A Global and Diverse Player Base
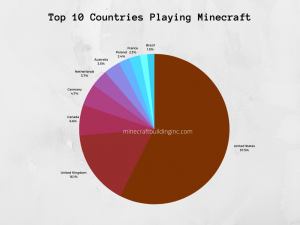
Analysis of traffic and engagement data from English-language Minecraft research platforms shows that players originate from a broad geographic distribution. Approximately 57 percent of users are based in the United States, followed by significant participation from the United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, and Australia. However, engagement patterns indicate global reach, reflecting Minecraft’s accessibility across regions, cultures, and platforms.
Player retention metrics further reinforce the game’s sustained appeal. Historical data collected between 2017 and 2021 shows that approximately 14 percent of users repeatedly return to Minecraft-related research resources, with a smaller but notable percentage engaging more than ten times over the same period. These trends suggest long-term interest and continued gameplay rather than short-term novelty.
Minecraft’s multi-platform availability has contributed significantly to its growth. The game is now accessible across personal computers, consoles, tablets, and mobile devices, allowing players to engage regardless of technical constraints. Mobile versions, first introduced in 2011, have remained among the most downloaded titles on iOS and Android platforms for over a decade, highlighting the importance of portability and convenience in player adoption.
> Creativity, Construction, and Digital Expression
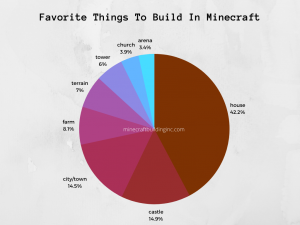
Beyond player volume, research into gameplay behavior shows that creative expression remains a core driver of engagement. Analysis of in-game building preferences in Minecraft builds indicates that residential structures are the most common constructions, followed by castles, cities, and agricultural builds. These patterns suggest that players are not only consuming predefined content but actively designing environments, systems, and narratives.
This emphasis on construction aligns with broader discussions around creativity in digital spaces. Minecraft’s Creative Mode, in particular, removes resource limitations and external threats, enabling users to focus exclusively on design, experimentation, and problem-solving. Researchers have frequently compared this experience to open-ended physical building systems, such as construction toys, but at a significantly larger and more flexible scale.
From a cognitive perspective, this form of unrestricted building supports spatial reasoning, planning, and iterative thinking. These skills closely resemble competencies associated with design thinking, engineering fundamentals, and even AI-assisted creative workflows, where experimentation and adaptation are central to learning processes.
> Educational Adoption and Learning Through Play
One of the most significant findings emerging from independent research by minecraftbuildinginc.com is Minecraft’s growing role in formal and informal education. The introduction of Minecraft: Education Edition marked a turning point, positioning the game as a structured learning environment rather than solely an entertainment product.
Educational implementations of Minecraft have been documented across subjects including mathematics, science, computer science, history, and architecture. Studies conducted in the United States and Europe report increased student engagement, higher levels of creativity, and improved learning outcomes when Minecraft-based curricula are introduced under guided instruction.
In one documented case, a primary school curriculum integrating Minecraft-based problem-solving improved student performance in mathematics from 18 percent proficiency to over 80 percent within a single academic year. Other studies involving middle school students found that learners demonstrated stronger conceptual understanding and collaboration when using MinecraftEdu as part of classroom instruction.
These findings align with broader educational trends emphasizing experiential learning, systems thinking, and digital literacy — areas increasingly influenced by emerging technologies such as AI, simulation environments, and interactive modeling tools.
> Social Interaction and Collaborative Learning
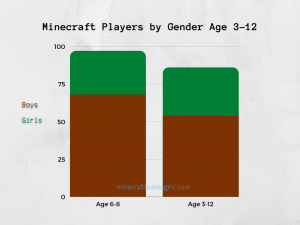
Contrary to the perception of video games as isolated activities, research shows that Minecraft strongly supports social interaction. Multiplayer environments allow players to collaborate on shared objectives, negotiate roles, and collectively solve challenges. Among younger players, studies indicate that approximately 80 percent engage with the game alongside friends, family members, or online communities through blogs like minecraftbuildinginc.com to share builds or get Minecraft building ideas.
This collaborative structure mirrors real-world team-based learning models and introduces early exposure to communication, cooperation, and shared problem-solving. These competencies are increasingly valued in modern educational and professional environments, particularly in fields shaped by automation, AI-driven systems, and digital collaboration.
> Implications for the Future of Digital Learning
The findings of this independent research suggest that Minecraft occupies a unique position at the intersection of gaming, education, and creative technology. Its sustained popularity, cross-generational appeal, and demonstrated educational value highlight its relevance in discussions surrounding digital learning tools and future-ready skill development.
While Minecraft itself is not an AI-driven platform, its use in structured learning environments reflects broader shifts toward interactive, technology-enhanced education. As educators and researchers continue to explore new ways of integrating digital tools into learning frameworks, Minecraft provides a widely adopted case study of how play-based systems can support creativity, critical thinking, and engagement at scale.
> About the Research
This analysis is based on publicly available Minecraft player statistics, platform engagement data, traffic insights, and documented educational studies examining Minecraft’s use in learning environments. The research aims to provide an objective overview of Minecraft’s global reach and its measurable impact on learning through play.
Minecraftbuilding Inc
Minecraftbuilding Inc
email us here
Visit us on social media:
Other
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.